Would you be interested to get FREE answer key for Carbon Cycle Gizmo questions?
If YES, check below for the right solutions…
Carbon Cycle Gizmo Answer Key (Student Exploration)
NOTE: All answers are checked twice before publishing them to you. So, please share if it helps you.
Vocabulary: atmosphere, biomass, biosphere, carbon reservoir, carbon sink, fossil fuel, geosphere, greenhouse gas, hydrosphere, lithosphere, photosynthesis.

Carbon Cycle Prior Knowledge Questions & Answers (Do these BEFORE using the Gizmo)
In the process of photosynthesis, plants intake… (Note: we are skipping the intro part so that we can directly jump into Q&A section)
Q.1. How do plants on Earth affect the amount of carbon in the Earth’s atmosphere?
Ans: Plants affect because the amount of carbon dioxide since they take it in and then process it into oxygen.
Q.2. Animals eat plants & produce CO2 & How do animals affect the amount of carbon in Earth’s atmosphere?
Ans: Animals increase the amount of carbon in the atmosphere.
Carbon Cycle Gizmo Warm-Up Questions & Answers
Q.1. From Earth’s atmosphere, where can the carbon atom go next?
Ans: Oceanic Co2, land plants(like trees and grass), & exposed rock.
Q.2. Click on Land plants and read the description (at the bottom of the simulation). How did the carbon atom get from the atmosphere to a plant?
Ans: By photosynthesis.
Q.3. Select Land animals. How did the carbon atom get from land plants into the animal (read the description )?
Ans: By consumption.
Q.4. Select Atmospheric CO2. How did the carbon atom get from land animals back to the atmosphere?
Ans: By cellular respiration.
Carbon Cycle Gizmo Answer Key – Activity A
Intro: Earth can be divided into 4 … (Note: we are skipping the intro part so that we can directly jump into Q&A section)
Q.1. Explore: Use the Gizmo to create a path for carbon (7 steps total) that begins and ends in the atmosphere. Fill in the steps in the path below. Then, summarize very briefly how the carbon atom got to that.
Ans: Find the answer from below image


Q.2. Create: Click Reset. Use the Gizmo to create a path in which the carbon atom goes from the atmosphere to the hydrosphere, biosphere, & geosphere(see the definition…). Describe each transition
Ans: Find the answer from below image
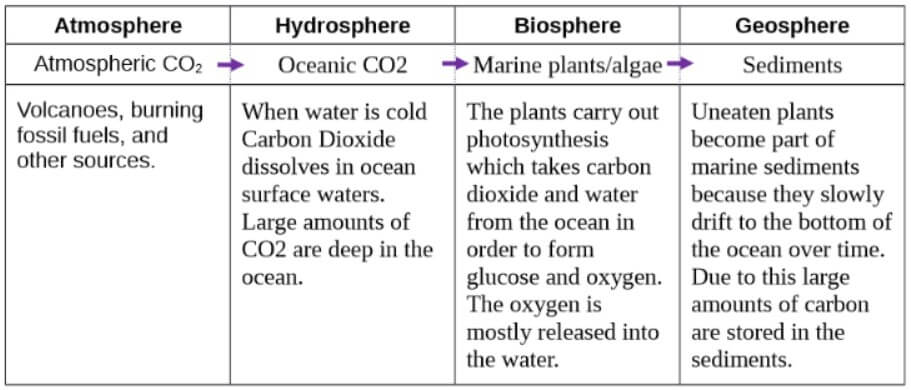
Q.3. Explore: Use the Gizmos to create three more (different) carbon paths, each starting and ending in the atmosphere. Label each location with A for atmosphere, B for biosphere, G for geosphere, or H for:
Ans: Find the answers below
Path 1: (A) Atmospheric CO2 → (B) land plants → (B) land animals → (A) atmospheric CO2
Path 2: (A) Atmospheric CO2→ (G) exposed rock → (H) oceanic CO2→ (B)marine plants/algae → (G) sediments →(P) petroleum →(A) lithosphere → (G) volcano → (A)Atmospheric CO2
Path 3: A) Atmospheric CO2→ (B)land plants → (G) coal → (P) power plant → (A) atmospheric CO2
Q.4. Explain: Based on the Gizmo, explain how the following transitions might take place:
Ans: Find answers to every question asked
A. Describe at least two ways that carbon can get from a land plant to the… It can get there from forest fires & land animals.
B. Describe at least two ways that carbon can get from the atmosphere to the hydrosphere… Carbon can get from the atmosphere to the hydrosphere by oceanic CO2 and through exposed rocks.
C. Can you find two ways that carbon can get from the ocean to the lithosphere? (The lithosphere is the rigid layer of the Earth, including the crust and part of the)… Two ways carbon can get from the ocean to the lithosphere is through the marine
plants and animals in the ocean, sediments, petroleum then to the lithosphere. The second way is through the shells and coral in the ocean, limestone, then to the lithosphere.
D. Describe at least two ways that carbon can get from seashells to the atmosphere… Two ways carbon can get from seashells to the atmosphere is through limestone, lithosphere, volcano, atmospheric CO2. The second way to get there would be through the oceanic CO2, marine animals and plants, sediments, natural gas, power plants, and then atmospheric CO2.
Carbon Cycle Gizmo Answer Key – Activity B
Intro: Fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, & natural gas… (Note: we are skipping intro part so that we can directly jump into Q&A section)
Q.1. Describe: Using the Gizmo, determine how coal and petroleum (oil) are Describe the steps required to form each fuel from atmospheric CO2.
Ans: Find the answers below
Coal: atmospheric CO2 + land plants + coal
Petroleum: atmospheric CO2 + oceanic CO2 +marine plants/algae + marine animals + sediments + petroleum
Q.2. Natural gas is a mixture of methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), and other gases. Find two ways that natural gas forms. List the steps of the two carbon pathways below:
Ans: Find the answers below
Path 1:[atmospheric CO2 + oceanic CO2 +marine plants/algae + sediments + natural gas+ atmospheric CH4]
Path 2:[limestone + lithosphere + exposed rocks + oceanic CO2 + marine plants/algae +sediments + natural gases]
A. How is the formation of natural gas related to the formation of coal and petroleum?… Coal and petroleum are both natural resources, that are very important to our daily lives.
Q.3. Describe: Fossil fuels are used in many Using the Gizmo, describe the main use for each fuel.
Ans: Find the answers below
Coal – Coal is used to fuel power plants and other machinery. It produces about 85% fossil fuel carbon.
Petroleum – Petroleum is used for electrical use and transporting.
Natural gas – Natural gas is used for transporting for a lot of household/everyday use.
A. In each case, what is the end product of burning the fossil fuel, and where does it go?… All the carbon builds up and causes pollution and they go back into the atmosphere.
Q.4. Explore: Another major contribution to atmospheric carbon dioxide is the cement industry. Using the Gizmo, find and list a carbon atom path from the atmosphere to the cement plant. (Hint: One of the ingredients in cement is )
Ans: Path: Atmospheric CO2 + exposed rocks + oceanic CO2 + shells/corals + limestone + cement plant
A. How is carbon dioxide produced in a cement plant?… Carbon dioxide is produced in a cement plant through calcination
Q.5. Analyze: Click Reset, then navigate to the Land animals. Select Atmospheric CH4.
Ans: Find answers to every question asked
A. How do land animals create methane?… Land animals create methane by “passing gas”.
B. Humans raise large numbers of cattle. How will these herds of cows affect Earth’s atmosphere?… These herds of cows can affect the atmosphere because they release large amounts of methane gas into the atmosphere
Q.6. Analyze: In many tropical rainforests, people clear land by cutting down trees and burning them. After a few years, the soil runs out of nutrients and cannot be farmed any How does this practice of “slash and burn agriculture” affect Earth’s atmosphere?
Ans: When we cut down trees it cuts down the amount of oxygen released into the atmosphere. Then when we burn things it releases more carbon into the air.
Q.7. Draw conclusions: In general, how do, many human activities influence the carbon cycle?
Ans: Human activities affect the cycle because we release carbon dioxide and our power plants, factories, transportation, and more affect what goes into the atmosphere.
Carbon Cycle Gizmo Answer Key – Activity C
Intro: We all know that humans have been burning fossil fuels… (Note: we are skipping intro part so that we can directly jump into Q&A section)
Q.1. Observe: The MODEL tab of the Gizmo shows a greatly simplified model of the carbon cycle. The ovals represent carbon reservoirs, where carbon is stored. The arrows represent the movement of carbon from one reservoir to another.
Ans: Find answers to every question asked
A. What are the two major sources of atmospheric carbon?… The two major sources of atmospheric carbon are initial atmospheric CO2 and plant biomass.
B. A carbon sink is a location that stores carbon for a long period of time. What are two carbon sinks that remove carbon from the atmosphere… The two carbon sinks that remove carbon from the atmosphere are oceans and plants.
C. The unit “GtC” stands for gigatonnes of carbon, where one GtC is equal to one trillion kilograms of carbon. Without making any changes to the Gizmo, list the carbon reservoirs from largest to smallest… Oceanic CO2 →Sediments →Fossil Fuels → Soil → Atmospheric CO2 → Land plants
Q.2. Experiment: If necessary, click Return to original settings. These settings approximate present-day conditions, but should not be taken as exact values.
Ans: Find answers to every question asked
A. What is the total amount of carbon removed from the atmosphere each year by the ocean and land plants?…Ocean – 2 Gtc & Land plants – 63 Gtc
B. What is the total amount of carbon added to the atmosphere from soil and the burning of fossil fuels?…Soil – 60 Gtc & Fossil fuels – 9 Gtc
C. How much will atmospheric carbon change in one year?… +4 Gtc… In 10 years?… +40 Gtc… In 100 years?… +400 Gtc
Q.3. Calculate: Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas that helps to trap heat in Earth’s atmosphere. We need some CO2 in the atmosphere to maintain a warm planet, but excess carbon can cause considerable warming of the planet.
Ans: Find answers to every question asked
A. What fossil fuel usage will result in no change in atmospheric CO2 each year?… Soil
B. What percentage decrease in fossil fuel usage is required to achieve this goal?… 100%
Q.4. Experiment: Using the Gizmo model, explore the following questions:
Ans: Find answers to every question asked
A. How does increasing plant biomass(amount of plants) affect atmospheric CO2?…It makes more plants, soil & quickens the rate of the process.
B. How does increasing oceanic CO2intake affect atmospheric CO2 and oceanic CO2?…It decreases CO2’s & oceanic CO2’s numbers.
Q.5. Infer: Click Reset and Return to original settings. Suppose we completely stopped burning fossil fuels immediately. How many years would it take to return to atmospheric CO2 levels from the year 1800, about 600 GtC? Use the Gizmo to find the answer
Ans: It would take around 200 years.
Q.6. Think about it: Since hard-shelled organisms evolved about 550 million years ago, billions of tons of limestone rock have been produced from their shells. Limestone is made of calcium carbonate, with the formula CaCO3. Based on this, how do you think the amount of atmospheric CO2has changed in the last 550 million years, & how has this affected Earth’s climate? Explain your answer.
Ans: I think that the amount of atmospheric CO2 has increased in the past 550 million years. I think the world has become more industrial and technology reliant, which isn’t always best for the environment. Our choices can sometimes leave a deeper step than we think.
Above are the correct answers for the Gizmo topic “Carbon Cycle“. Now let us bring you a glimpse of the Carbon Cycle & its different processes in the coming session.
Or would you like to explore other topics associated with Gizmos, then check the link below:
About Carbon Cycle Concept
The carbon cycle is the process that moves carbon atoms between the Earth’s atmosphere, biosphere, lithosphere, and oceans.
Carbon is a key element in all life on Earth and plays an important role in regulating our planet’s climate.
The carbon cycle is constantly in flux, with CO2 being released into the atmosphere through volcanic eruptions and photosynthesis, and then being taken up by plants and animals before eventually being deposited back into the ground or ocean.
Human activities like mining and burning fossil fuels have disrupted the natural carbon cycle, causing CO2 levels to rise to unprecedented levels.
This has led to global warming and climate change, which poses a serious threat to human health and our environment.
We need to take steps to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and promote sustainable practices that will help to restore the balance of the carbon cycle.
There are many things we can do to reduce our carbon footprint and help to combat climate change.
Some simple steps include driving less, recycling, composting, and using energy-efficient appliances.
We can also support policies that encourage renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
By working together, we can create a more sustainable future for our planet and ourselves.
More References:
=> https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_cycle
Thank you for reading! we hope the summary has provided you with some useful information about Carbon Cycle that may help in answering the above questions as well.
Hope you find Carbon Cycle Gizmo Answer Key for levels A, B & C by following our answers above. Share with your batchmates if you find it helpful.

Hi, I’m Thomas, and I’ve been a teacher for over 10 years and have taught students at all levels. I created this blog to really help students get ahead of their exams as well as provide helpful guides on various courses.
